Historical Analysis of Presidential Polls
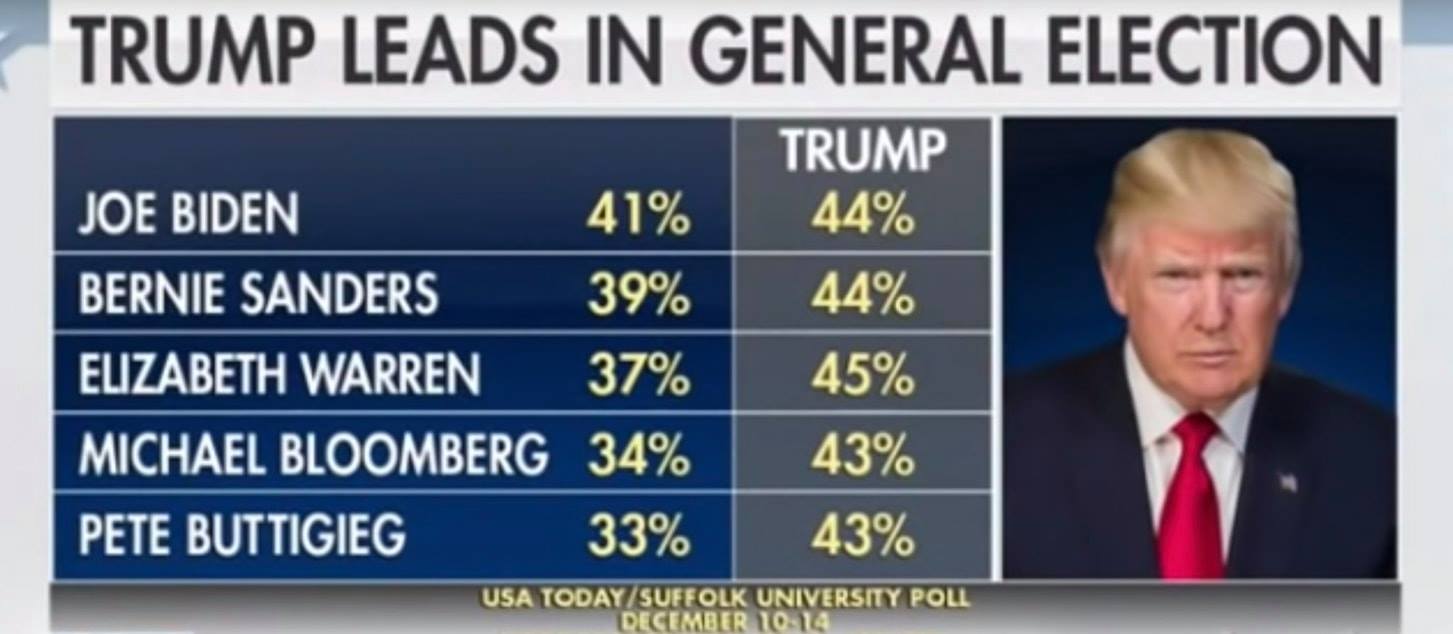
Presidential polls have a long and storied history in the United States, dating back to the early 1900s. The first known presidential poll was conducted by the Literary Digest in 1916, and it correctly predicted the winner of the election, Woodrow Wilson. Since then, presidential polls have become an essential part of the electoral process, providing valuable insights into the preferences of voters and the likely outcome of elections.
There are many different types of presidential polls, each with its own unique methodology. Some of the most common types of polls include:
- Telephone polls: These polls are conducted by calling a random sample of voters and asking them a series of questions about their voting preferences.
- Online polls: These polls are conducted online, and they allow voters to participate from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Mail polls: These polls are conducted by sending a questionnaire to a random sample of voters and asking them to return it by mail.
The results of presidential polls are often used to predict the outcome of elections. However, it is important to note that polls are not always accurate. There are a number of factors that can affect the accuracy of a poll, including the size of the sample, the methodology used, and the timing of the poll.
Despite the potential for error, presidential polls remain an important tool for understanding the preferences of voters and the likely outcome of elections. By providing valuable insights into the electoral process, polls help to inform campaign strategies and ensure that the voices of voters are heard.
Evolution of Presidential Polls
Presidential polls have evolved significantly over the years. In the early days, polls were conducted primarily by newspapers and magazines. However, in the 1930s, the advent of radio and television led to the development of new polling techniques. These new techniques allowed pollsters to reach a larger number of voters and to conduct polls more quickly and efficiently.
In the 1960s, the development of computer technology led to further advances in polling methodology. Computers allowed pollsters to analyze data more quickly and accurately, and they also made it possible to conduct more complex polls.
Today, presidential polls are conducted using a variety of methods, including telephone, online, and mail. Pollsters also use a variety of statistical techniques to analyze data and to predict the outcome of elections.
Use of Polling Data in Campaign Strategies
The results of presidential polls are often used by campaign strategists to develop their campaign strategies. By understanding the preferences of voters, strategists can make informed decisions about which issues to emphasize, which candidates to run, and how to allocate their resources.
For example, if a poll shows that a particular candidate is trailing in the polls, the candidate’s campaign strategists may decide to change their strategy. They may decide to focus on different issues, to run a more aggressive campaign, or to spend more money on advertising.
Polling data can also be used to identify swing voters. Swing voters are voters who are undecided or who are leaning towards one candidate but could be persuaded to vote for another candidate. By targeting swing voters, campaign strategists can increase their chances of winning an election.
Presidential polls are an essential tool for campaign strategists. By providing valuable insights into the preferences of voters, polls help strategists to develop effective campaign strategies and to increase their chances of winning elections.
Factors Influencing Presidential Poll Results
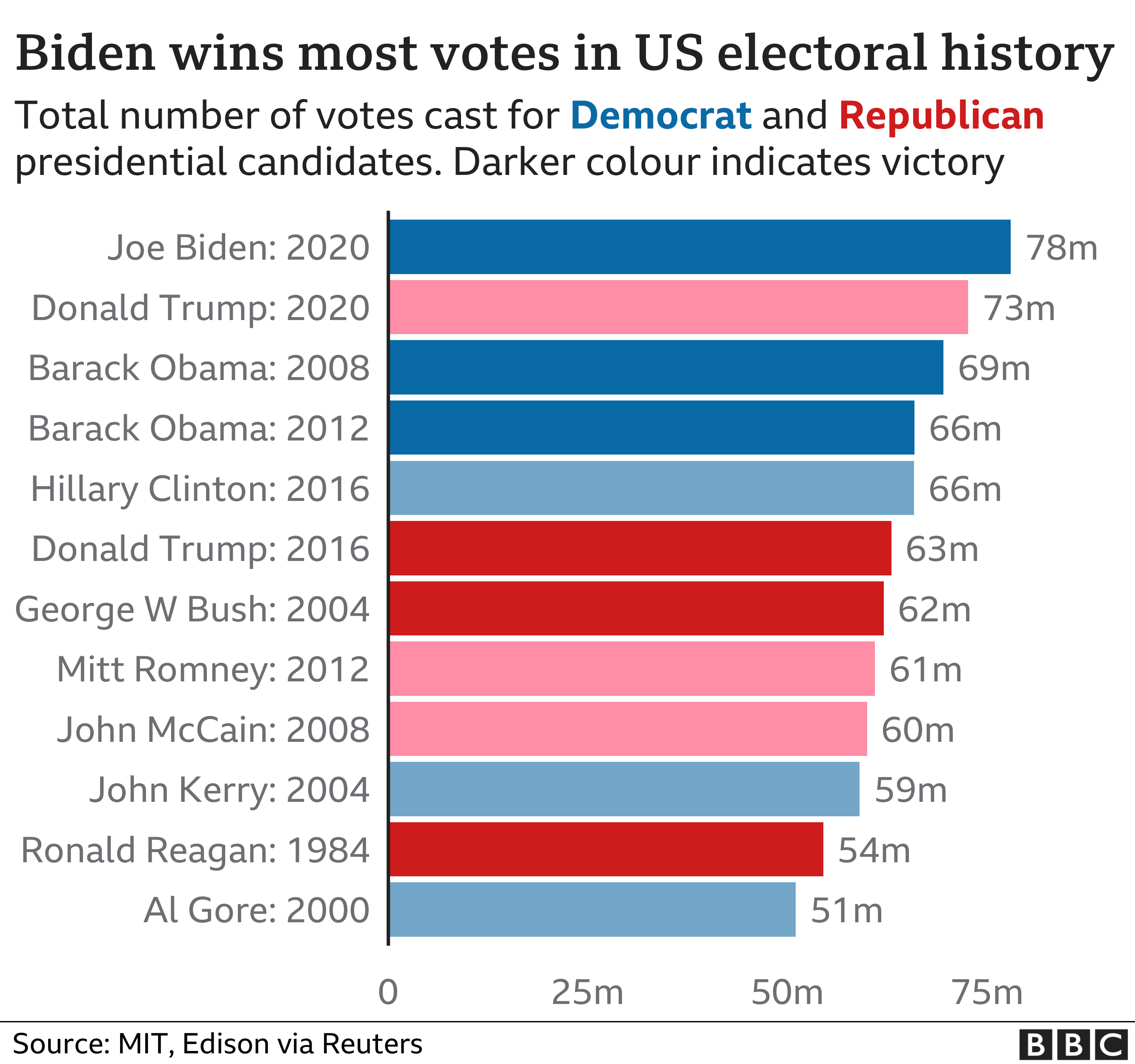
The accuracy of presidential polls is influenced by various factors, including sample size, question wording, and respondent demographics. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting poll results and assessing their reliability.
Sample Size
Sample size refers to the number of respondents included in a poll. Larger sample sizes generally produce more accurate results because they are less likely to be influenced by random fluctuations or sampling errors. Smaller sample sizes, on the other hand, may not accurately represent the entire population, leading to potential bias.
Question Wording
The wording of poll questions can significantly impact the results. Leading questions, for instance, can influence respondents’ answers by suggesting a particular outcome or viewpoint. Biased or ambiguous questions can also introduce errors into the data.
Respondent Demographics
The demographic characteristics of respondents, such as age, gender, education, and income, can influence poll results. Different demographic groups may have varying opinions on political issues, and polls that fail to accurately represent the demographics of the population may produce biased results.
Potential for Bias and Error
Despite efforts to conduct polls objectively, bias and error can still occur. Non-response bias arises when certain segments of the population are less likely to participate in polls, leading to an underrepresentation of their views. Sampling error refers to the difference between the results of a poll and the true population values, which is influenced by sample size and random variation.
Impact of External Events and Media Coverage
External events, such as major news stories or political scandals, can influence poll results by shifting public opinion. Media coverage can also play a role, as it can shape how respondents perceive candidates and issues. Polling data should be interpreted with caution in the context of such events and media influences.
Using Presidential Polls for Strategic Decision-Making
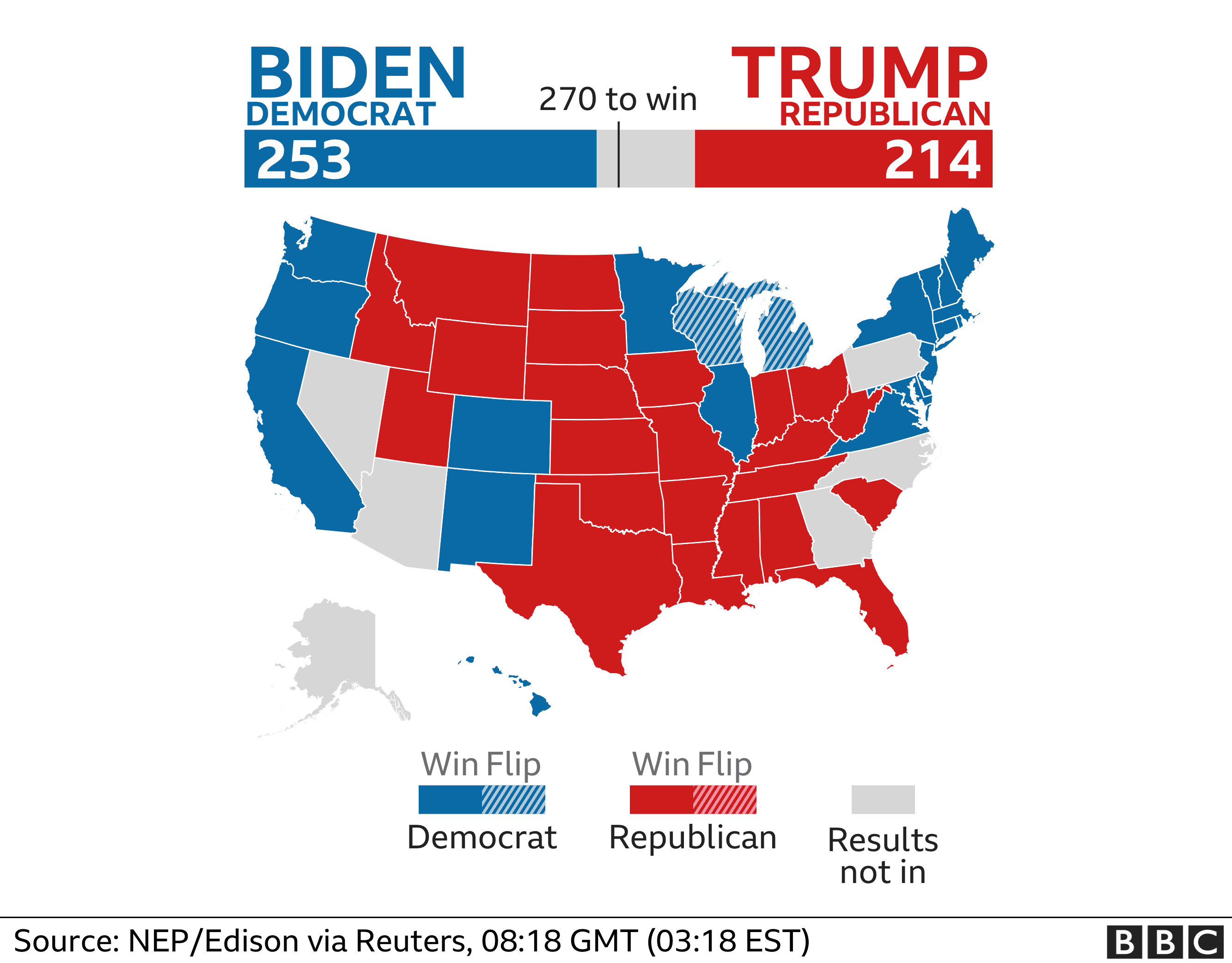
Presidential polls play a pivotal role in modern election campaigns, providing candidates and their teams with valuable insights into voter sentiment and trends. These polls help shape campaign strategies, target messaging, and allocate resources effectively.
Polls offer a snapshot of public opinion at a specific point in time, allowing candidates to gauge their popularity, identify areas of strength and weakness, and track changes over time. By analyzing poll data, campaigns can make informed decisions about:
Targeting Voters, Presidential polls
Poll data can help campaigns identify key voter demographics and geographic regions where they need to focus their efforts. By understanding which groups are most likely to support them, campaigns can tailor their messaging and outreach strategies accordingly.
Adjusting Campaign Messaging
Polls can also inform campaign messaging. By monitoring public opinion on specific issues, candidates can adjust their platforms and talking points to resonate better with voters. For example, if a poll shows that voters are concerned about healthcare, a candidate may prioritize healthcare in their campaign speeches and advertising.
Allocating Resources
Poll data can assist campaigns in allocating resources strategically. By identifying areas where they have strong support, campaigns can focus their spending on those regions and voter groups. This data-driven approach helps maximize the impact of campaign funds.